( Source : George S. Yip, Anderson Graduate School of Management, UCLA, 1994)
Definition of competitive advantage : = Ability to outperform rivals on (potential) profitability.
(Robert M Grant, Contemporary Strategy Analysis, Bassil Blackwell)
The pentagon of competitive advantage :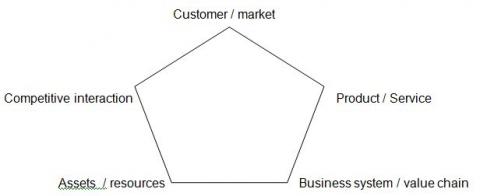
When we carefully analyze each of these 5 components we will be able to find a valid competitive advantage, and if already found, assess if it is sustainable.
The hexagon of competitive advantage :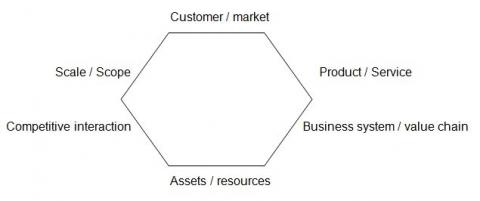
Note that this hexagon adds the “scale/scope” dimension, which is critical for any strategic analysis.
But competitive advantages fade out, or get worn out in time. Competitors do not stand still, and the environment changes. The strategic task then becomes to keep on developing new sources of competitive advantage !
The strategic dilemma :
How do you select what advantages to try to develop ? MARKET AND COMPETITIVE ANALYSIS
How do you decide whether you can do it ? RESOURCE & COMPETENCE ANALYSIS
How do you make it happen ? IMPLEMENTATION MANAGEMENT
As we have seen in the prior blogs, there are basically two strategic positions - low cost, and differentiation. Here are some features that help to coherently organize the enterprise :
DESIRED ORGANIZATION FEATURES FOR GENERIC LOW COST STRATEGIES :
Organization structure | Centralized authority and functions Flat, minimal layers Support / overhead focused and limited |
Management processes | Mechanisms to monitor and control manufacturing and logistics costs Market information for sales intelligence and pricing Planning for capital expenditures Understanding competitors´ costs Performance evaluation and variable compensation tied to unit margin (sales and costs) |
People | Functional specialization for process improvement Few staff Use of external resources to variabilize costs Promoting from within |
Culture | Innovation and creativity for process improvement Customer focus Lean and mean |
DESIRED ORGANIZATION FEATURES FOR GENERIC DIFFERENTIATION STRATEGIES :
Organization structure | Tendency to decentralize Multiple function business units More support and overhead focused on market opportunities |
Management processes | Mechanisms to monitor and measure new product success Extensive marketing information Planning for market share and product development Understanding competitors´ products and services Performance evaluation and variable compensation tied to creating and realizing new opportunities |
People | Multiple functional experiences More staff Use of consultants for broader market information Hiring from outside to penetrate new markets |
Culture | Innovation and creativity for new products Built in slack to encourage new ideas Customer focus |
